ENDURE
The project
Endure is a 2.5 M€ ERC Consolidator Grant project aiming to develop a novel fuse-based segmentation design approach to arrest the propagation of failures in building structures.
Key Challenges
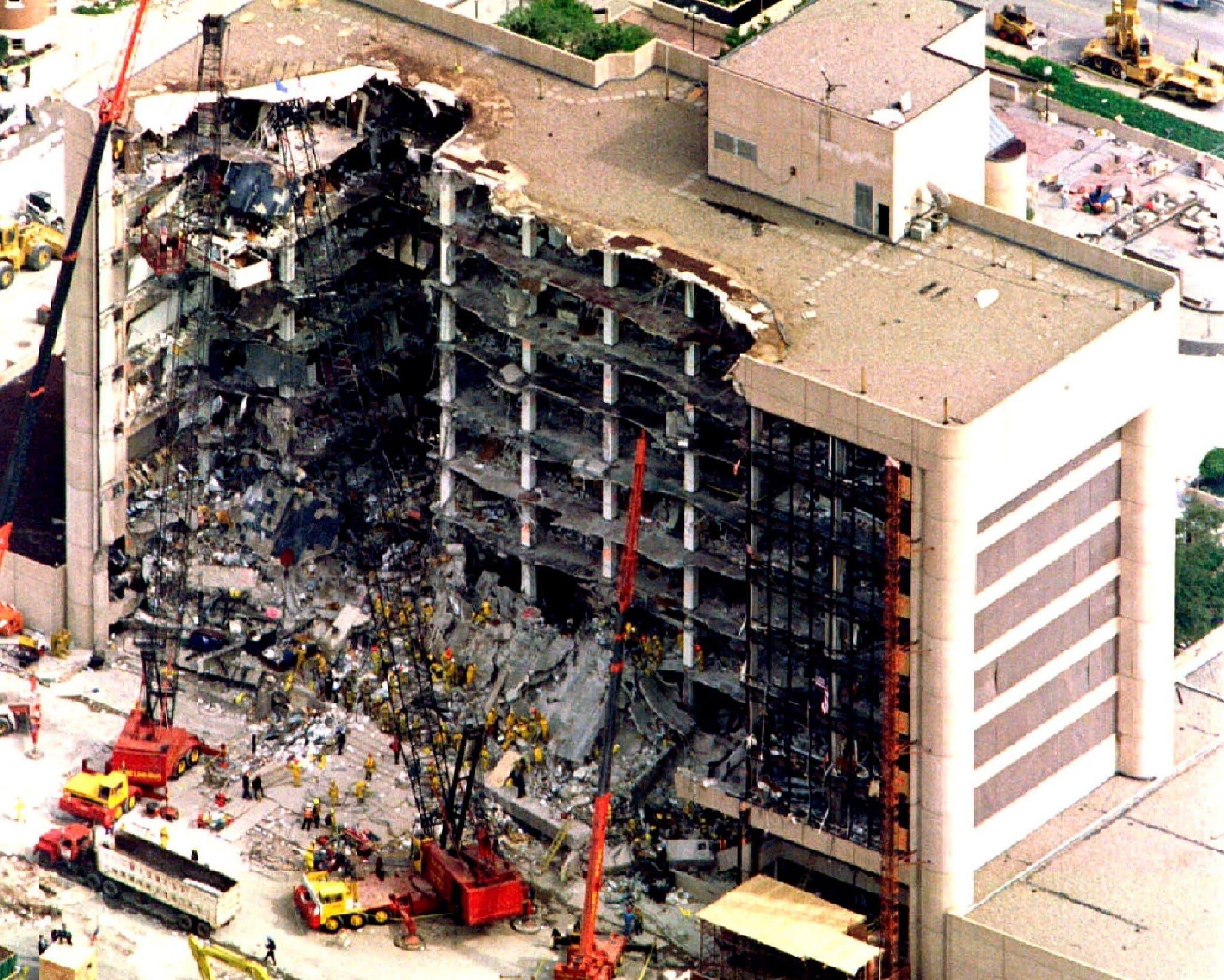
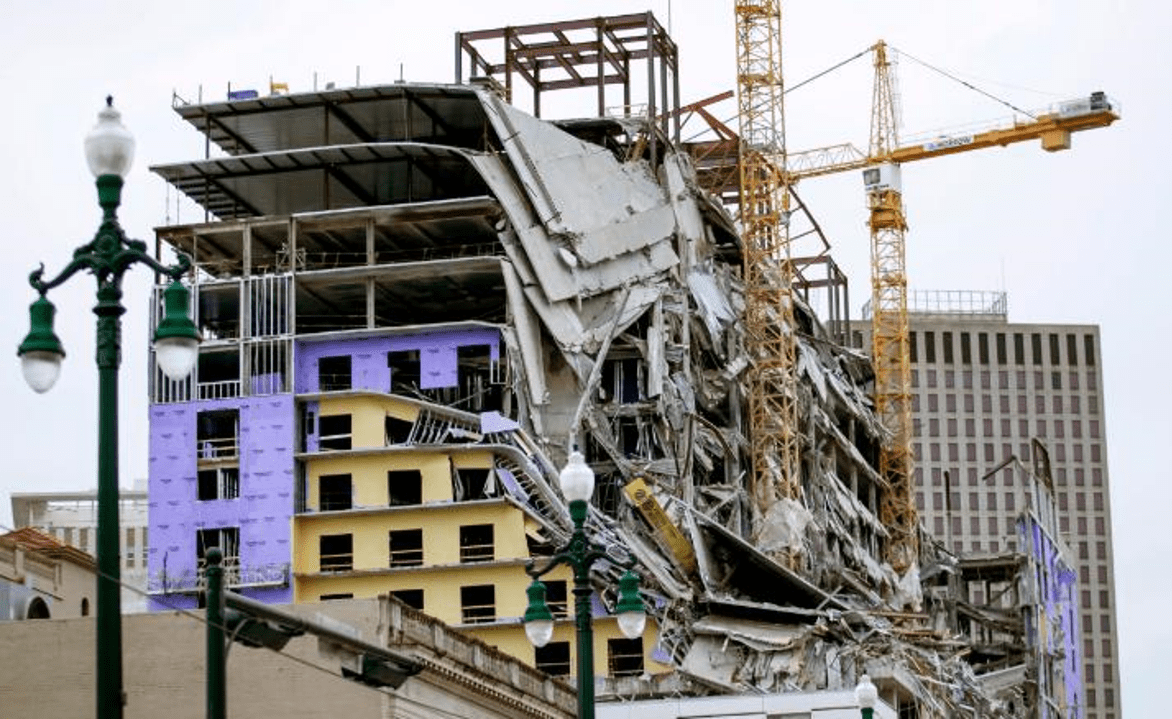
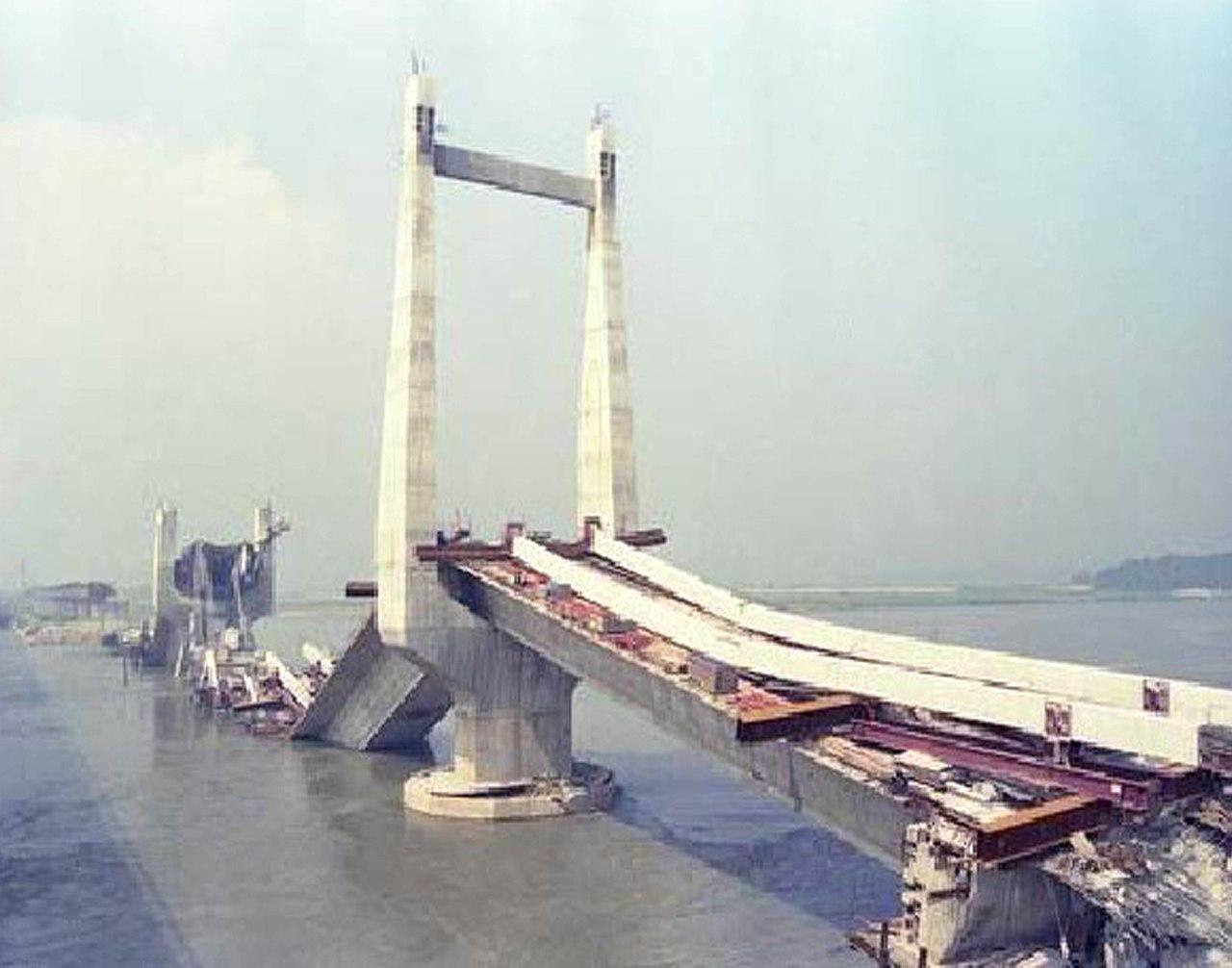
Achieving resilient societies requires designing buildings and infrastructures able to withstand and recover from extreme abnormal events. Such events often cause local-initial damage to critical elements of building structures, followed by a cascade of further failures in the rest of the building; a phenomenon known as “progressive collapse”
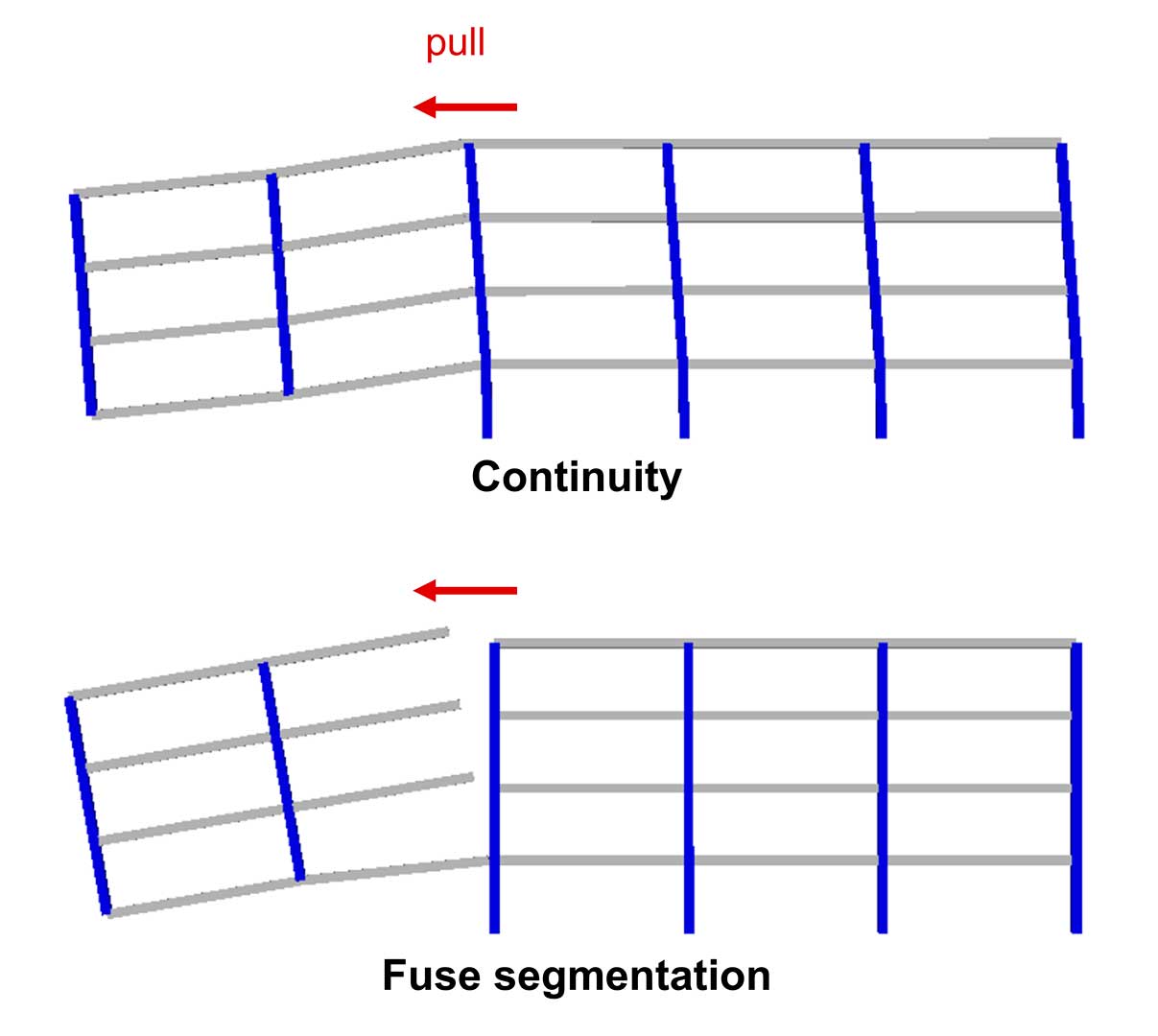
Current building design philosophies for avoiding progressive collapse aim to define alternative load paths (ALPs) to redistribute the loads supported by failed elements to the rest of the structure. This is normally achieved by providing a building with extensive continuity through suitable tying systems.
Although this strategy has been shown to be valid in certain situations (e.g. small initial failure), there are other situations (e.g. initial failure of several columns, large initial blast loading) in which the ties can help to propagate a local failure and lead to total collapse.
It is therefore both urgent and necessary to define new design approaches to remedy these limitations to mitigate the risk of disaster and improve the security of our buildings.



Structural fuses
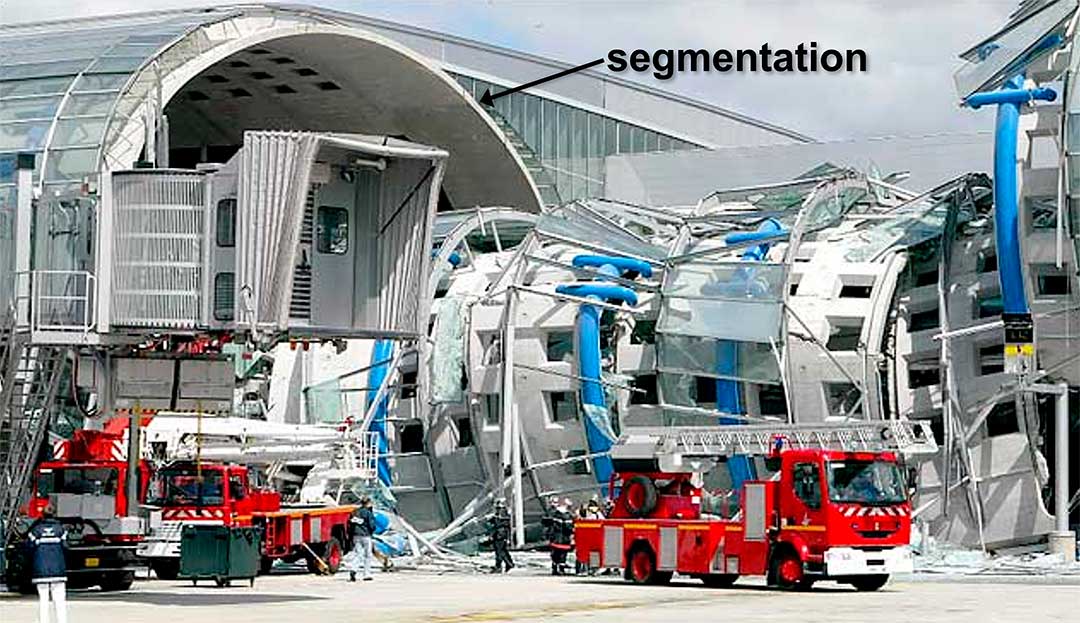
There have been many cases in which a local-initial failure caused by an extreme event has not spread to other parts of the building thanks to it being segmented i.e. since the structure is divided into separate parts with no intervening continuity, the failure or collapse of one zone has no effect on the others (e.g. partial collapse in the Charles de Gaulle Airport in 2004). Although segmentation has been seen to work well in a number of cases, it was not in fact purposely adopted to avoid progressive collapse and has hardly been mentioned in the scientific literature.
However, segmentation (e.g. by expansion joints) could be counter-productive by breaking continuity, since continuity has demonstrated to work well for small initial failure scenarios.
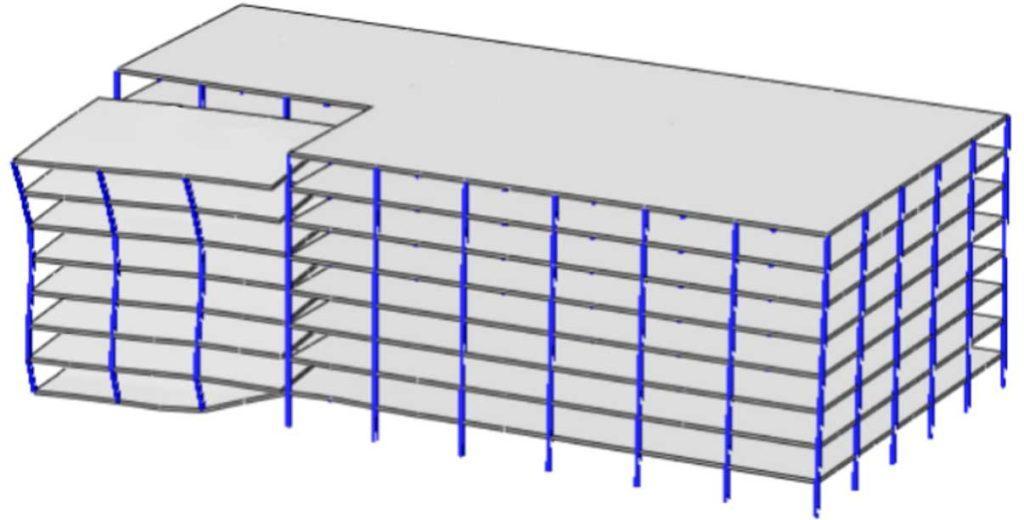
The Endure project thus aims to develop a novel fuse-based segmentation design approach which combines, for the first time, the advantages of two opposite concepts: continuity and segmentation.
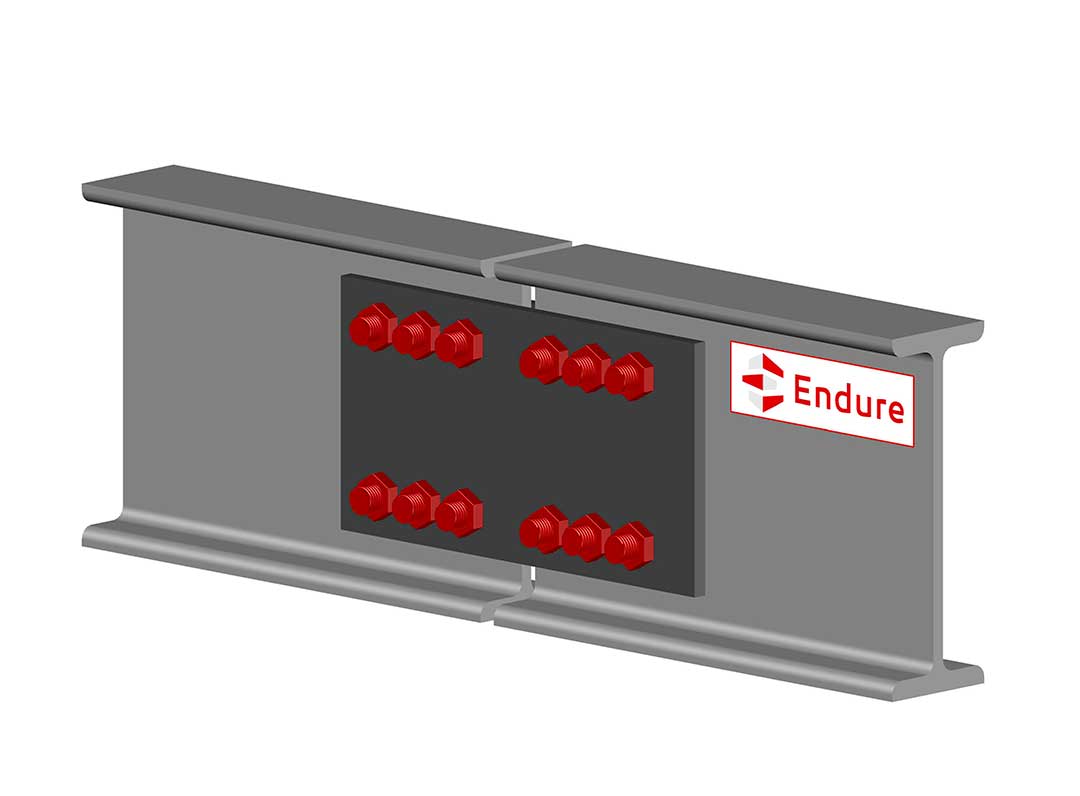
This radically different approach involves connecting building segments with structural fuses that will provide continuity for normal loads or small initial failures, but will separate when failure propagation is inevitable.
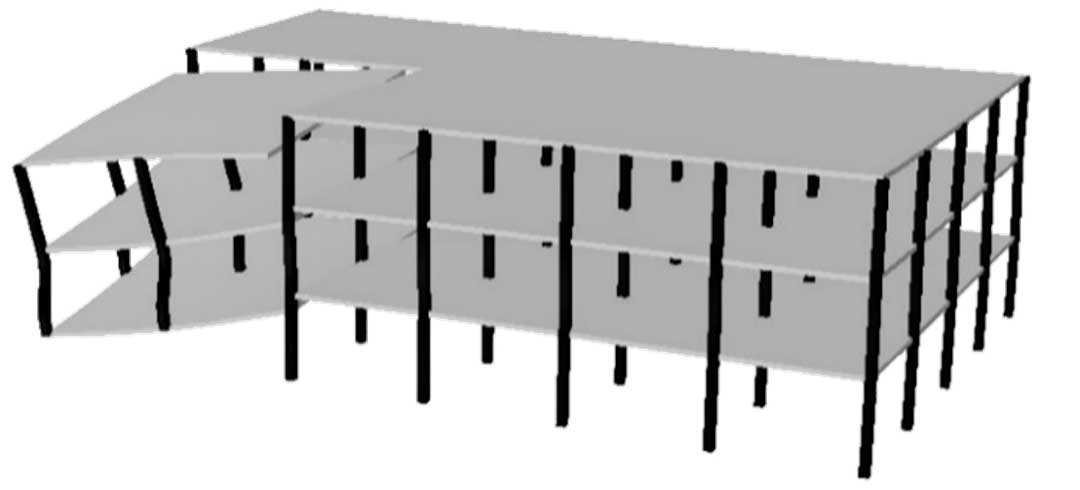

Objectives
Endure aims to revolutionise the design of robust buildings with a novel fuse-based segmentation approach. To achieve this central goal, the project is focused on the following four specific objectives:
- To develop a performance-based approach for the design of fuse-segmented buildings.
- To design, manufacture and test fuses for segmenting buildings.
- To implement fuses in segmented building structures and to validate and test the new fuse-based approach in realistic building prototypes.
- To engage with industry experts and code-issuing entities, and disseminate-communicate the project’s outcomes.
Methodology
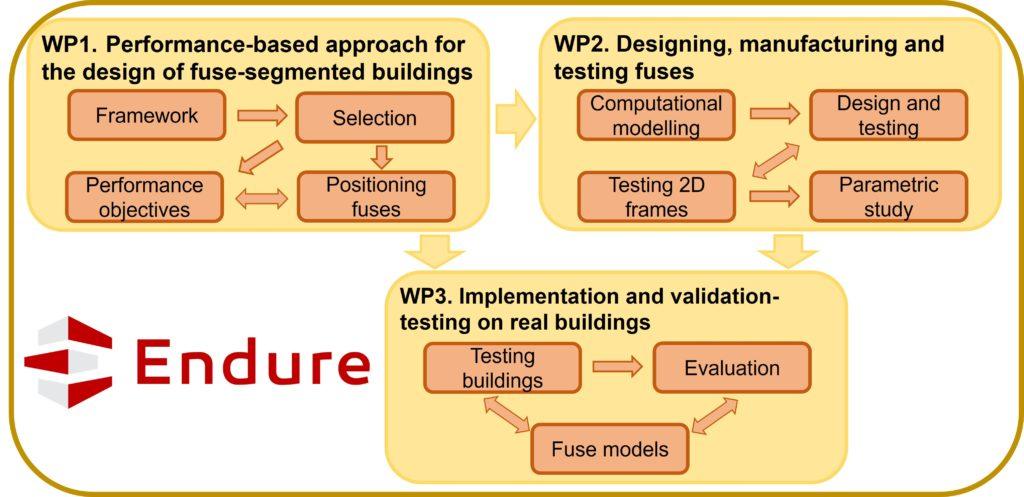
Endure has been structured into four Work Packages (WPs) that are directly related to each of its defined objectives.
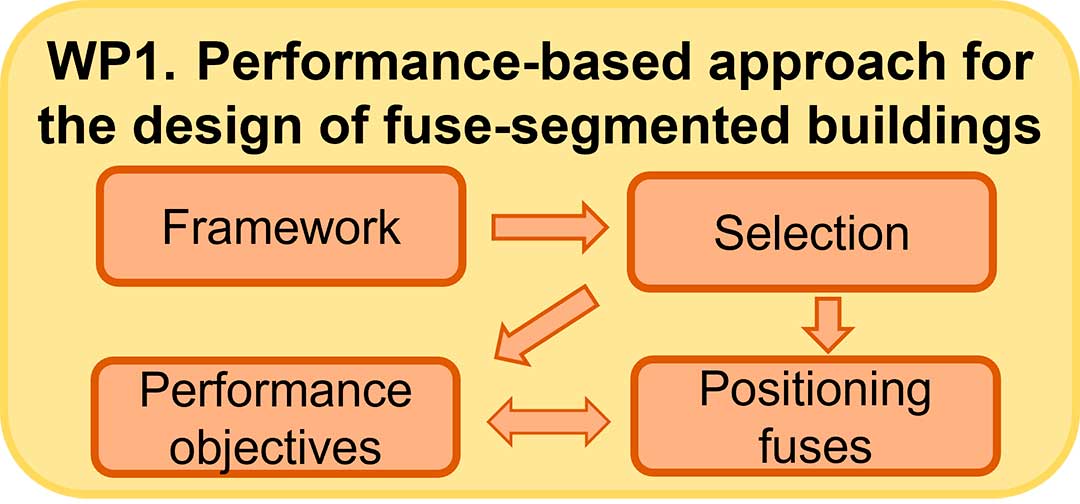
WP 1. Performance-based approach for the design of fuse-segmented buildings
This WP is mainly concerned with the development of novel methodologies for identifying buildings in which segmentation would be advantageous, for structural robustness design using segmentation, and for the positioning of fuses. The proposed approach will involve a risk-based evaluation of robustness which considers the probability of different events and their associated consequences.
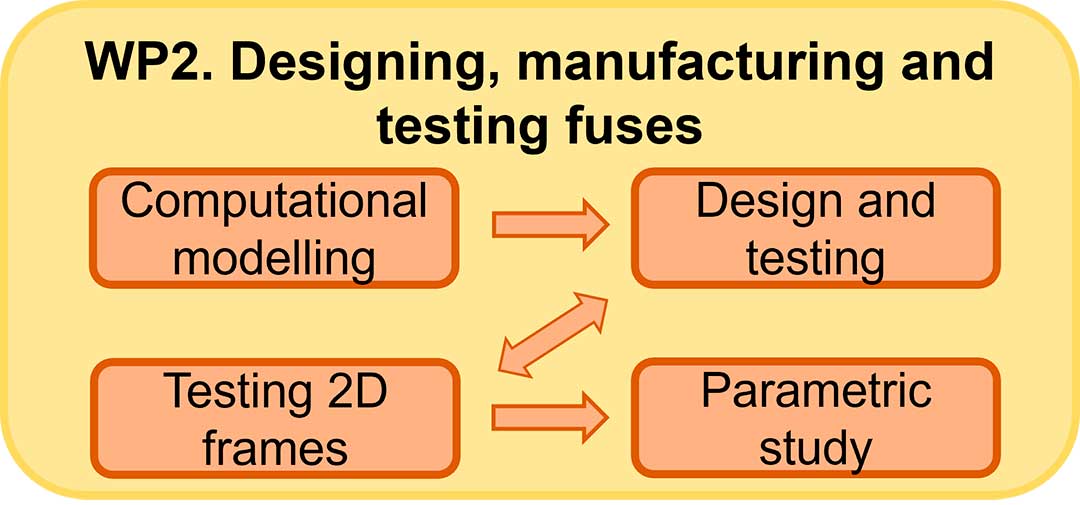
WP 2. Designing, manufacturing and testing fuses
In WP2, fuse requirements will be defined through advanced computational simulations before proceeding to their design, manufacturing and assembly. This involves a series of lab-tests both prior and posterior to the definition of the required detailing for their implementation in buildings. A computational parametric study will also be undertaken to extrapolate the fuse-based segmentation design to a range of different design situations.
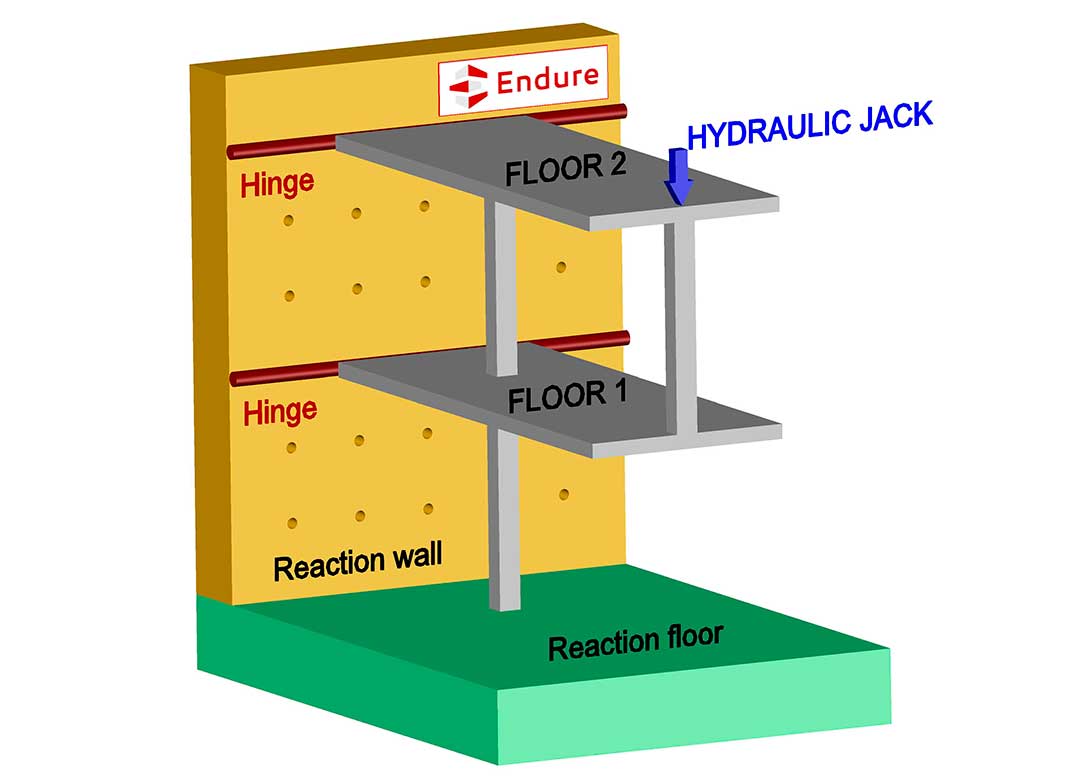
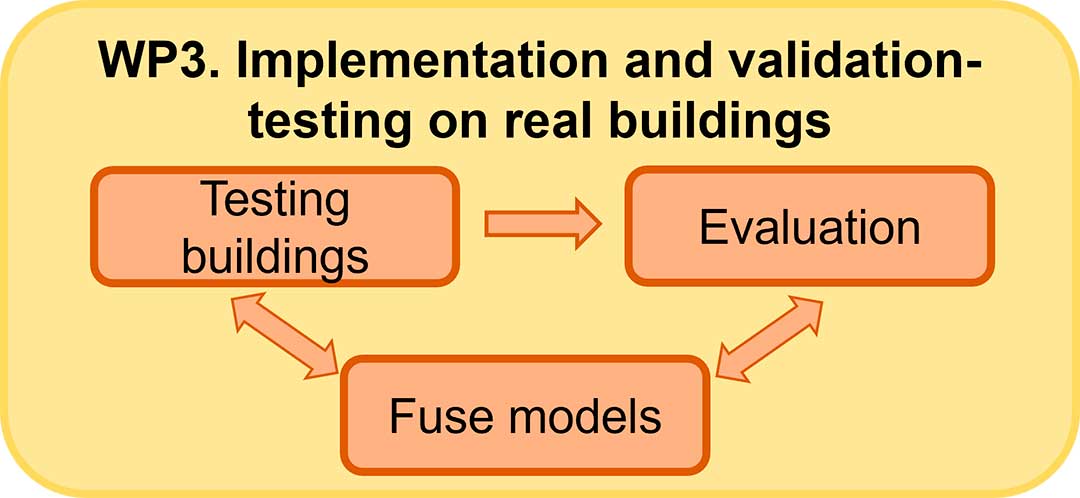
WP 3. Implementation and validation-testing on real buildings
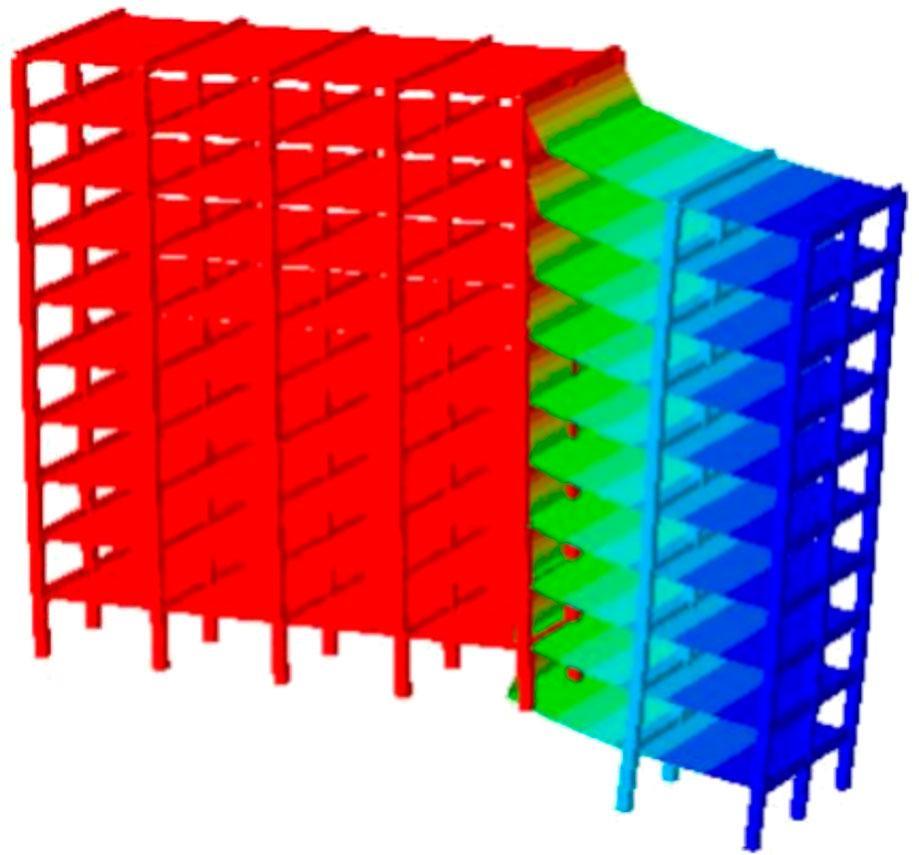
This WP includes the ambitious task of testing two full-scale fuse-segmented buildings to validate the new design philosophy in real situations. Computational simulations of different event scenarios will then be performed to check that the fuses will only trigger in extreme situations (large initial failure) while the building’s overall behaviour remains unaffected under normal loads or small initial failure. Simplified calculation models will then be defined to facilitate the inclusion of fuses in everyday building design.
Impact
Endure can be expected to have a considerable impact in scientific, technological and social fields:
- Scientifically, the fuse-based segmentation approach to be developed clearly has the potential to revolutionise the present robust building design philosophies which focus on giving the structure continuity, redundancy and ductility. This will open up a new research area since it can be foreseen that the new approach will require further studies for large-scale implementation.
- Technologically, the project will open up new patent development channels in the form of fuses, and new robust building design and construction procedures. Companies as well as standards-issuing entities will be clearly benefitted by these results.
- Societally, the project will lead to safer buildings, especially in the case of extreme events with severe consequences for structural integrity. In addition, given that any innovation in the design and construction of infrastructures has a large impact on the economy, the outcomes of Endure can ultimately be expected to produce considerable economic gain.